Table of Contents:
1. Introduction: Understanding the Importance of Surge Arresters
2. What is a Surge Arrester?
3. Types of Surge Arresters
3.1 Type 1 Surge Arresters
3.2 Type 2 Surge Arresters
3.3 Type 3 Surge Arresters
4. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Surge Arrester
4.1 Voltage Rating
4.2 Discharge Current Rating
4.3 Response Time
4.4 Mounting Location
4.5 Environmental Considerations
5. How to Determine Your Lightning Protection Needs
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6.1 What is the purpose of a surge arrester?
6.2 How does a surge arrester work?
6.3 Can surge arresters prevent damage to electrical equipment?
6.4 Do surge arresters require regular maintenance?
6.5 Can surge arresters protect against all types of electrical surges?
7. Conclusion
1. Introduction: Understanding the Importance of Surge Arresters
In today's technology-driven world, protecting our electronic devices and electrical systems from sudden power surges is of utmost importance. Lightning strikes can cause irreparable damage to sensitive equipment, leading to costly repairs or replacements. This is where surge arresters come into play. By diverting excessive electrical energy from lightning strikes, surge arresters safeguard your property, ensuring the longevity and reliability of all connected electrical devices.
2. What is a Surge Arrester?
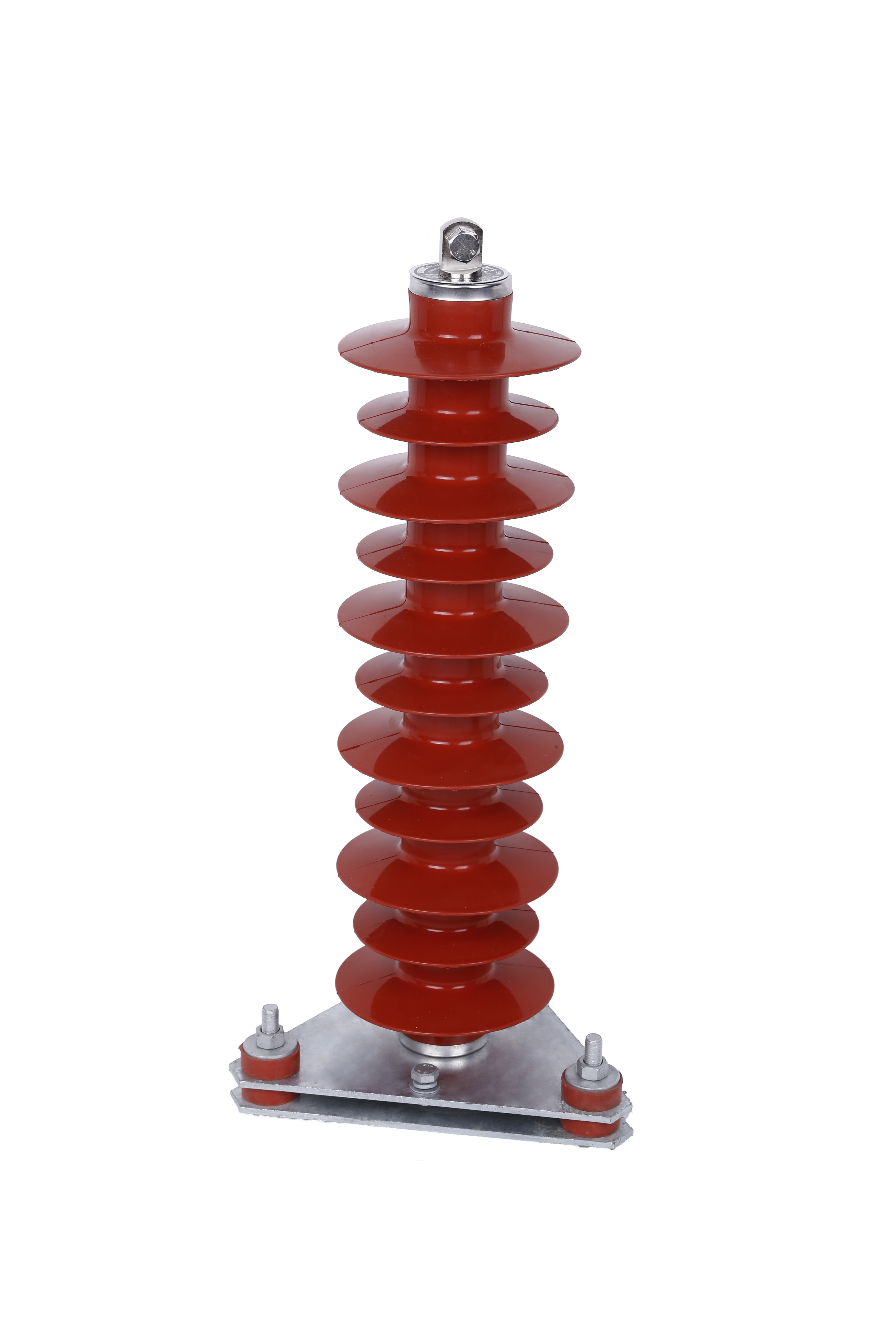
A surge arrester, also known as a lightning arrester or surge protector, is a device designed to dissipate high voltage surges caused by lightning strikes or other electrical disturbances. It acts as a shield, redirecting the extra energy away from your electrical system and grounding it safely. A surge arrester provides a pathway for the excess electrical energy, protecting your valuable equipment from potential damage.
3. Types of Surge Arresters
When it comes to choosing the right surge arrester for your lightning protection needs, it's crucial to understand the different types available. Here are the three main types of surge arresters:
3.1 Type 1 Surge Arresters
Type 1 surge arresters, also known as "primary surge arresters," are designed to protect against direct lightning strikes. They are typically installed at the service entrance of a building to safeguard the entire electrical system from high voltage surges. Type 1 surge arresters offer the highest level of protection and are essential for properties located in areas prone to frequent lightning strikes.
3.2 Type 2 Surge Arresters
Type 2 surge arresters, also known as "secondary surge arresters," are installed at the distribution board or sub-panel level. They protect specific areas or equipment within a building, such as HVAC systems, appliances, or electronic devices. Type 2 surge arresters provide an additional layer of protection, complementing the primary surge arrester's role in safeguarding your electrical system.
3.3 Type 3 Surge Arresters
Type 3 surge arresters, also known as "point-of-use surge protectors," are designed to protect individual electrical devices or equipment. They are commonly used in conjunction with Type 2 surge arresters to provide localized protection. Type 3 surge arresters are ideal for sensitive devices like computers, televisions, or home entertainment systems, as they prevent electrical surges from reaching these devices.
4. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Surge Arrester
When selecting a surge arrester, several crucial factors must be taken into account to ensure optimal protection for your lightning protection needs. Consider the following:
4.1 Voltage Rating
The surge arrester's voltage rating should match or exceed the maximum voltage of your electrical system. It is crucial to select a surge arrester with the appropriate voltage rating to ensure effective protection against overvoltage events.
4.2 Discharge Current Rating
The discharge current rating indicates the surge arrester's capacity to handle high currents during a surge event. It is essential to choose a surge arrester with a discharge current rating suitable for your specific lightning protection needs.
4.3 Response Time
The response time of a surge arrester defines how quickly it can divert excess electrical energy from a surge event. A faster response time ensures better protection for your equipment. Look for surge arresters with low response times to minimize the risk of damage.
4.4 Mounting Location
Consider where the surge arrester will be installed. Surge arresters can be mounted at the service entrance, distribution board, or directly on individual devices. The mounting location should be strategically chosen to provide the most effective protection for your entire electrical system.
4.5 Environmental Considerations
Take into account the environmental conditions in which the surge arrester will be installed. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to harsh elements can affect the arrester's performance and lifespan. Choose surge arresters that are designed to withstand the specific environmental conditions of your location.
5. How to Determine Your Lightning Protection Needs
To determine your specific lightning protection needs, a professional assessment is recommended. Lightning protection specialists can evaluate your property's vulnerability to lightning strikes and recommend the appropriate surge arresters and lightning protection measures. Factors such as geographical location, building structure, and the electrical system's complexity will be taken into consideration to ensure comprehensive lightning protection.
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6.1 What is the purpose of a surge arrester?
A surge arrester's primary purpose is to protect electrical systems and devices from high voltage surges caused by lightning strikes or other electrical disturbances. It diverts excessive electrical energy away from the system, preventing damage to sensitive equipment.
6.2 How does a surge arrester work?
Surge arresters work by providing a low-impedance path for the surge current to flow safely to the ground. When a surge occurs, the arrester's internal components, typically metal oxide varistors (MOVs), rapidly change their resistance to allow the excess electrical energy to be safely dissipated.
6.3 Can surge arresters prevent damage to electrical equipment?
While surge arresters provide effective protection against high voltage surges, they cannot guarantee 100% prevention of damage. However, they significantly reduce the risk of equipment damage by diverting excess energy and limiting the voltage that reaches connected devices.
6.4 Do surge arresters require regular maintenance?
Surge arresters are generally maintenance-free devices. However, regular inspections by qualified professionals are recommended to ensure their proper functioning. Visual inspections and testing can identify any signs of damage or degradation and ensure that the surge arresters are in optimal condition.
6.5 Can surge arresters protect against all types of electrical surges?
Surge arresters are designed to protect against high voltage surges, including those caused by lightning strikes. However, they may not provide adequate protection against other types of electrical disturbances such as power surges caused by faulty electrical wiring or equipment. It is important to have a comprehensive lightning protection system in place to address all potential sources of electrical surges.
7. Conclusion
Choosing the right surge arrester for your lightning protection needs is crucial in safeguarding your property and electrical equipment from the devastating effects of lightning strikes. By considering factors such as voltage rating, discharge current rating, response time, mounting location, and environmental considerations, you can make an informed decision to ensure optimal protection. Remember to consult with lightning protection specialists to assess your specific needs and implement a comprehensive lightning protection system. With the right surge arrester in place, you can have peace of mind knowing that your property is well-protected against lightning-induced power surges.
1. Introduction: Understanding the Importance of Surge Arresters
2. What is a Surge Arrester?
3. Types of Surge Arresters
3.1 Type 1 Surge Arresters
3.2 Type 2 Surge Arresters
3.3 Type 3 Surge Arresters
4. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Surge Arrester
4.1 Voltage Rating
4.2 Discharge Current Rating
4.3 Response Time
4.4 Mounting Location
4.5 Environmental Considerations
5. How to Determine Your Lightning Protection Needs
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6.1 What is the purpose of a surge arrester?
6.2 How does a surge arrester work?
6.3 Can surge arresters prevent damage to electrical equipment?
6.4 Do surge arresters require regular maintenance?
6.5 Can surge arresters protect against all types of electrical surges?
7. Conclusion
1. Introduction: Understanding the Importance of Surge Arresters
In today's technology-driven world, protecting our electronic devices and electrical systems from sudden power surges is of utmost importance. Lightning strikes can cause irreparable damage to sensitive equipment, leading to costly repairs or replacements. This is where surge arresters come into play. By diverting excessive electrical energy from lightning strikes, surge arresters safeguard your property, ensuring the longevity and reliability of all connected electrical devices.
2. What is a Surge Arrester?
A surge arrester, also known as a lightning arrester or surge protector, is a device designed to dissipate high voltage surges caused by lightning strikes or other electrical disturbances. It acts as a shield, redirecting the extra energy away from your electrical system and grounding it safely. A surge arrester provides a pathway for the excess electrical energy, protecting your valuable equipment from potential damage.
3. Types of Surge Arresters
When it comes to choosing the right surge arrester for your lightning protection needs, it's crucial to understand the different types available. Here are the three main types of surge arresters:
3.1 Type 1 Surge Arresters
Type 1 surge arresters, also known as "primary surge arresters," are designed to protect against direct lightning strikes. They are typically installed at the service entrance of a building to safeguard the entire electrical system from high voltage surges. Type 1 surge arresters offer the highest level of protection and are essential for properties located in areas prone to frequent lightning strikes.
3.2 Type 2 Surge Arresters
Type 2 surge arresters, also known as "secondary surge arresters," are installed at the distribution board or sub-panel level. They protect specific areas or equipment within a building, such as HVAC systems, appliances, or electronic devices. Type 2 surge arresters provide an additional layer of protection, complementing the primary surge arrester's role in safeguarding your electrical system.
3.3 Type 3 Surge Arresters
Type 3 surge arresters, also known as "point-of-use surge protectors," are designed to protect individual electrical devices or equipment. They are commonly used in conjunction with Type 2 surge arresters to provide localized protection. Type 3 surge arresters are ideal for sensitive devices like computers, televisions, or home entertainment systems, as they prevent electrical surges from reaching these devices.
4. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Surge Arrester
When selecting a surge arrester, several crucial factors must be taken into account to ensure optimal protection for your lightning protection needs. Consider the following:
4.1 Voltage Rating
The surge arrester's voltage rating should match or exceed the maximum voltage of your electrical system. It is crucial to select a surge arrester with the appropriate voltage rating to ensure effective protection against overvoltage events.
4.2 Discharge Current Rating
The discharge current rating indicates the surge arrester's capacity to handle high currents during a surge event. It is essential to choose a surge arrester with a discharge current rating suitable for your specific lightning protection needs.
4.3 Response Time
The response time of a surge arrester defines how quickly it can divert excess electrical energy from a surge event. A faster response time ensures better protection for your equipment. Look for surge arresters with low response times to minimize the risk of damage.
4.4 Mounting Location
Consider where the surge arrester will be installed. Surge arresters can be mounted at the service entrance, distribution board, or directly on individual devices. The mounting location should be strategically chosen to provide the most effective protection for your entire electrical system.
4.5 Environmental Considerations
Take into account the environmental conditions in which the surge arrester will be installed. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to harsh elements can affect the arrester's performance and lifespan. Choose surge arresters that are designed to withstand the specific environmental conditions of your location.
5. How to Determine Your Lightning Protection Needs
To determine your specific lightning protection needs, a professional assessment is recommended. Lightning protection specialists can evaluate your property's vulnerability to lightning strikes and recommend the appropriate surge arresters and lightning protection measures. Factors such as geographical location, building structure, and the electrical system's complexity will be taken into consideration to ensure comprehensive lightning protection.
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6.1 What is the purpose of a surge arrester?
A surge arrester's primary purpose is to protect electrical systems and devices from high voltage surges caused by lightning strikes or other electrical disturbances. It diverts excessive electrical energy away from the system, preventing damage to sensitive equipment.
6.2 How does a surge arrester work?
Surge arresters work by providing a low-impedance path for the surge current to flow safely to the ground. When a surge occurs, the arrester's internal components, typically metal oxide varistors (MOVs), rapidly change their resistance to allow the excess electrical energy to be safely dissipated.
6.3 Can surge arresters prevent damage to electrical equipment?
While surge arresters provide effective protection against high voltage surges, they cannot guarantee 100% prevention of damage. However, they significantly reduce the risk of equipment damage by diverting excess energy and limiting the voltage that reaches connected devices.
6.4 Do surge arresters require regular maintenance?
Surge arresters are generally maintenance-free devices. However, regular inspections by qualified professionals are recommended to ensure their proper functioning. Visual inspections and testing can identify any signs of damage or degradation and ensure that the surge arresters are in optimal condition.
6.5 Can surge arresters protect against all types of electrical surges?
Surge arresters are designed to protect against high voltage surges, including those caused by lightning strikes. However, they may not provide adequate protection against other types of electrical disturbances such as power surges caused by faulty electrical wiring or equipment. It is important to have a comprehensive lightning protection system in place to address all potential sources of electrical surges.
7. Conclusion
Choosing the right surge arrester for your lightning protection needs is crucial in safeguarding your property and electrical equipment from the devastating effects of lightning strikes. By considering factors such as voltage rating, discharge current rating, response time, mounting location, and environmental considerations, you can make an informed decision to ensure optimal protection. Remember to consult with lightning protection specialists to assess your specific needs and implement a comprehensive lightning protection system. With the right surge arrester in place, you can have peace of mind knowing that your property is well-protected against lightning-induced power surges.